|
~
|
Highlight events 2022
15/07/2022
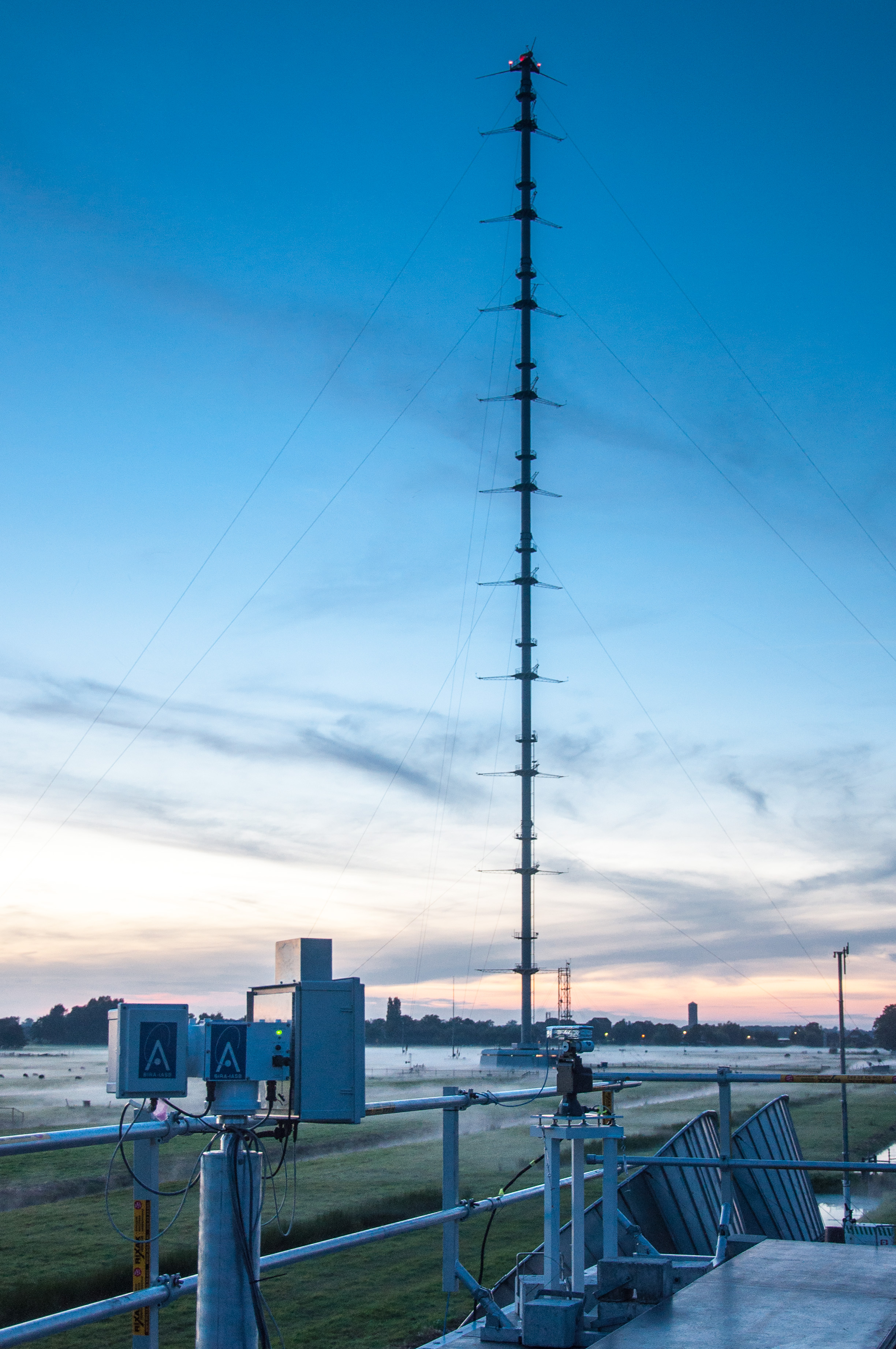
The SIJAQ campaign in South Korea. The Geostationary Environmental Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) was launched into space by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER) and the Ministry of Environment of Korea, on board the GEO-KOMPSAT 2B satellite in 2019. GEMS is one of three air quality monitoring missions over the Asian continent. To validate the measurements from this instrument, two ground based campaigns have been organized so far: SIJAQ/GMAP in 2021 and SIJAQ 2022 this year. 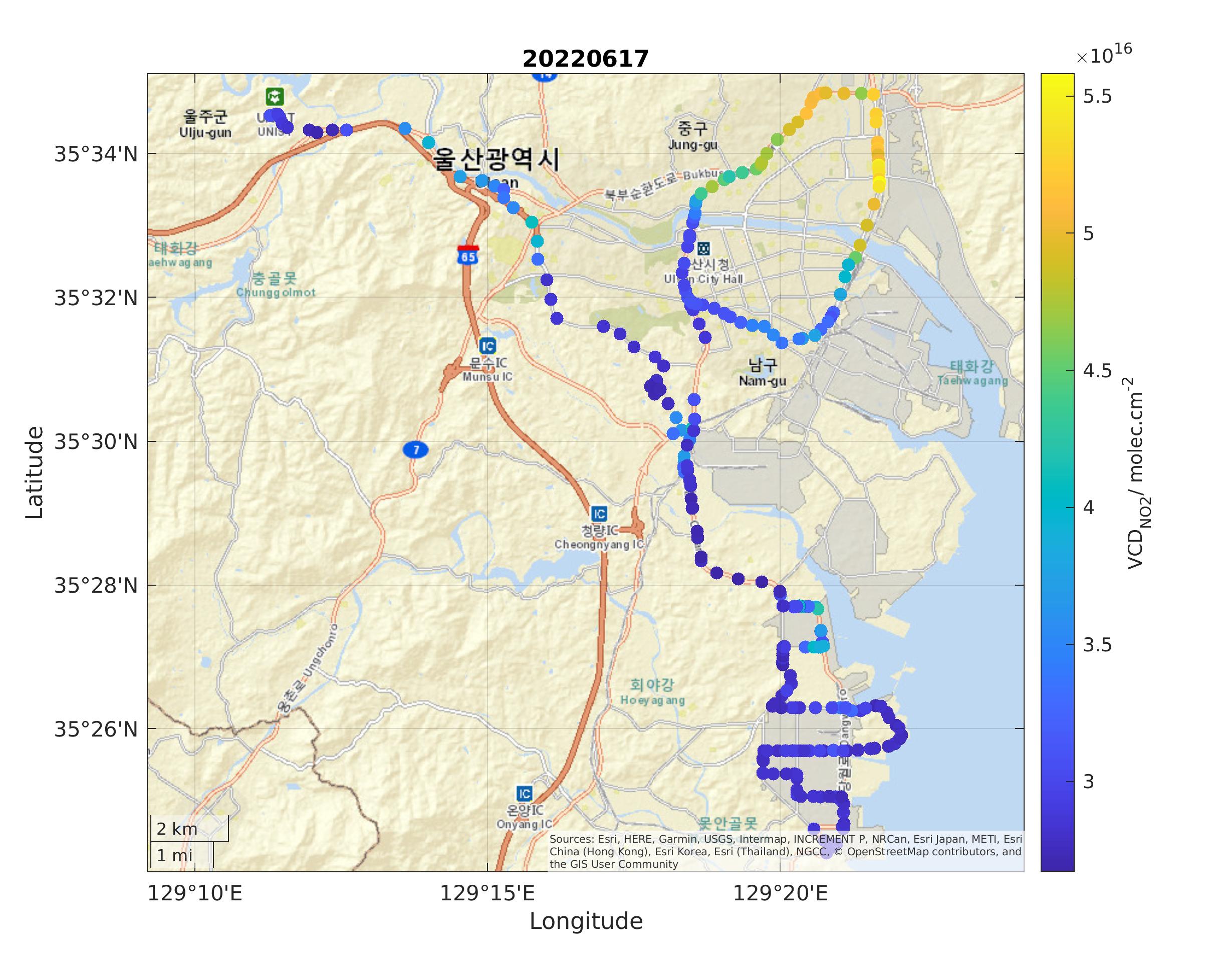
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB 2021
19/11/2021
Detecting new SO2 sources with COBRA In order to monitor and estimate global atmospheric sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, accurate and sensitive detetion of this trace gas from space is highly important. Traditionally the detection of SO2 is done with the DOAS technique [1]. Although this method has faitfully been applied in the retrieval of SO2 from satellite for years, it is accopanied by substantial biases (requiring a post-retrieval offset-correction) and noise levels. Inspired by detection methods applied in the thermal infrared spectral domain, a new algorithm for the retrieval of SO2 columns from satellite observations in the ultraviolet spectral range was recently proposed in a highlight paper in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics (ACP, [2]). The retrieval scheme is based on a measurement error covariance matrix to fully represent the radiance variability over SO2-free areas, so that the SO2 slant column density is the only retrieved parameter of the algorithm. The validity of this approach, named COBRA, was demonstrated on measurements from the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) aboard the Sentinel-5 Precursor (S-5P) satellite. The method significantly reduces both the noise and biases present in the current TROPOMI operational DOAS SO2 retrievals. 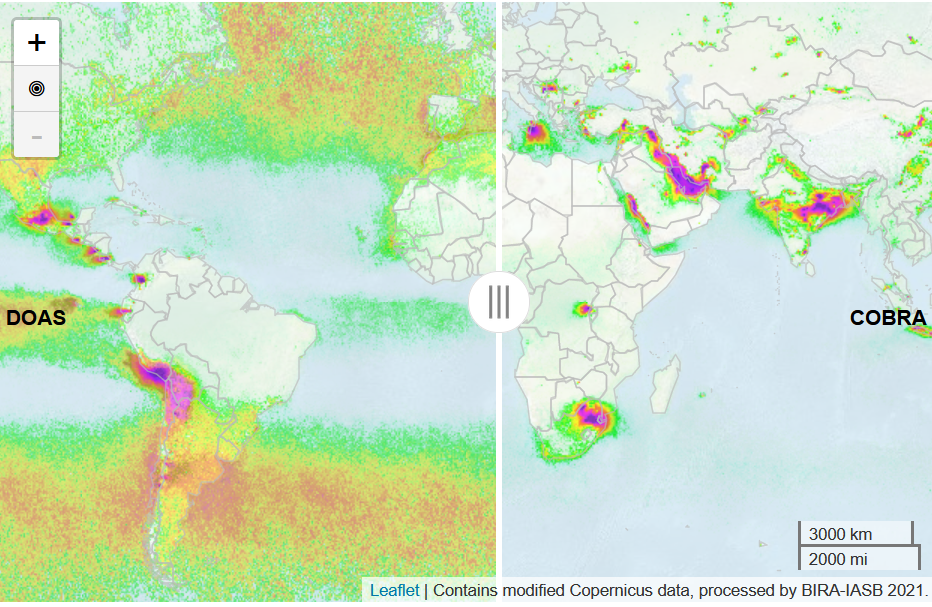
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB
06/07/2021
The NITROCAM campaign. This past spring, we have conducted and coordinated an airborne measurement campaign called NITROCAM, in cooperation with the Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the Freie Universität Berlin (FUB)...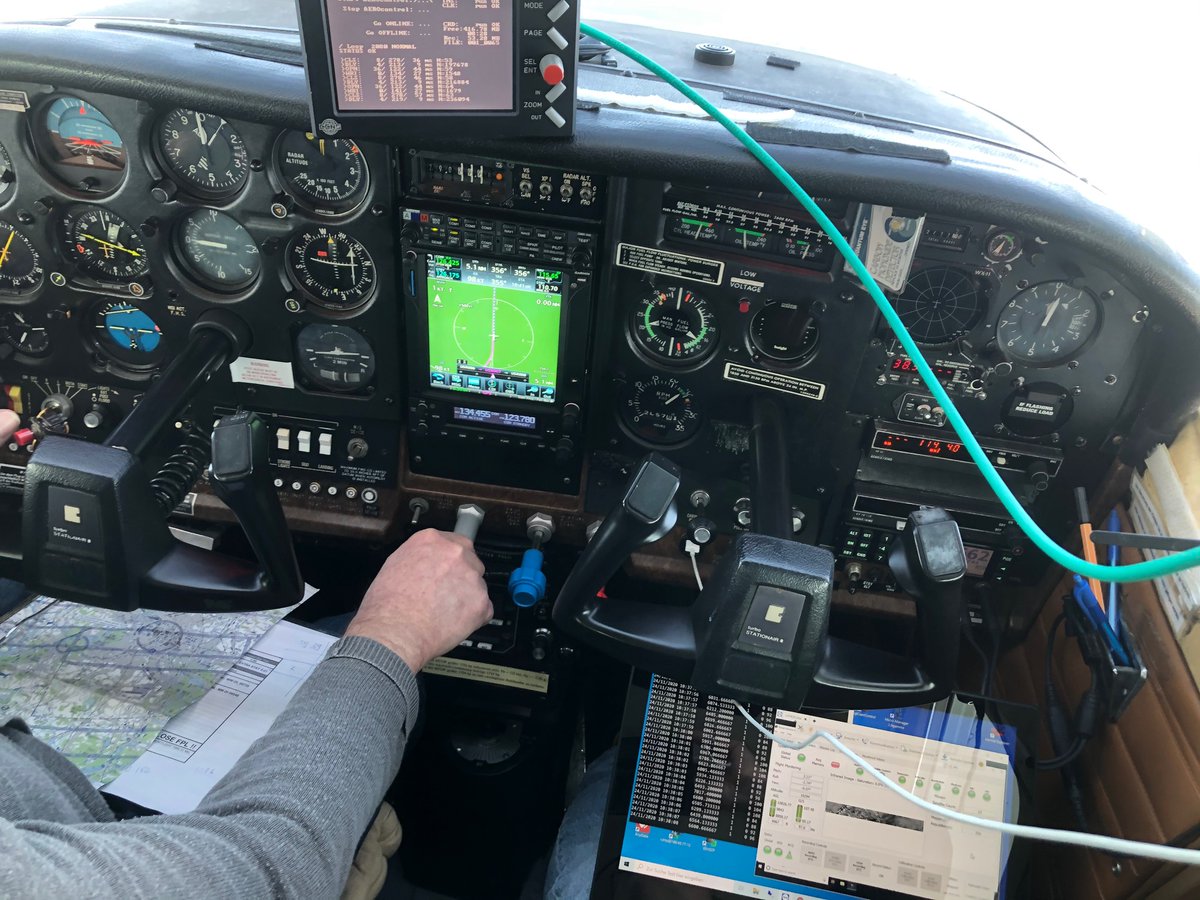 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB
22/04/2021
Detecting ship emissons: the SEMPAS project. Recently BIRA launched a project to develop an instrument, called SEMPAS (Ship Emission Monitoring by Passive Absorption Spectroscopy), to remotely measure NO2, SO2 and CO2 emissions from individual ships, from which the fuel sulfur content (FSC) can be quantified.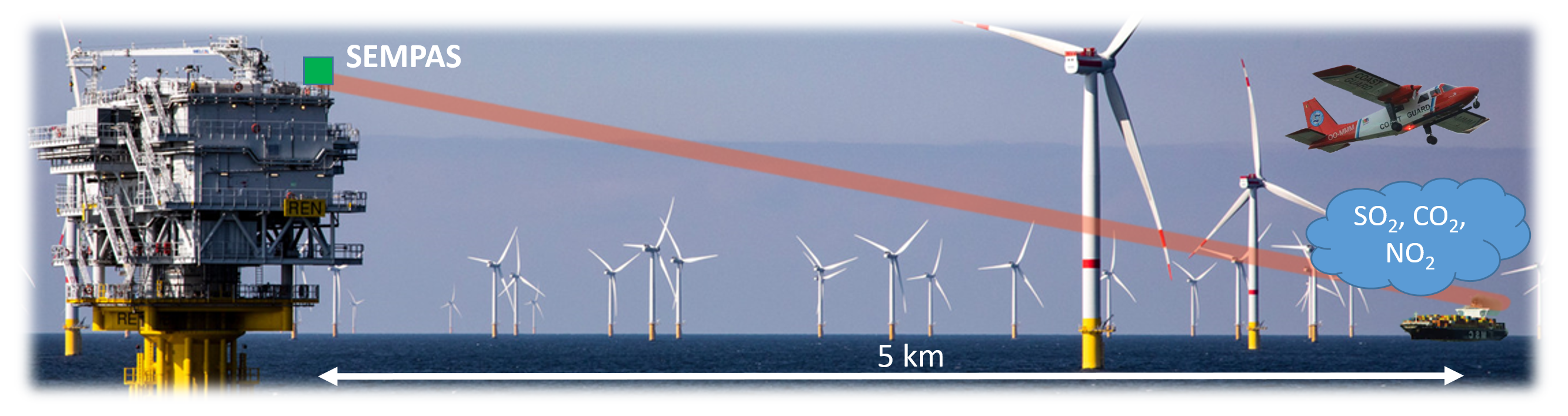 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB 2020
21/09/2020
Global nitrous acid emissions by wildfires revealed from space.
On Monday September 21, 2020, the prestigious Nature Geosciences journal published an article presenting the
first satellite detection of nitrous acid (HONO) using the TROPOMI satellite instrument.

Ⓒ BIRA-IASB
18/09/2020
Chemical species in California wildfires observed from space. During the summer season, forest fires are a natural part of the climate and landscape of the western USA. Recent years have seen a prolonged fire season with increased intensity and extent of the fire events in comparison to a 'normal' season. The 2020 fire season so far has shown intense and widespread fire events and may be registered as one of the worst seasons ever recorded. BIRA-IASB has been following the chemical gas species released from the wildfires by means of the TROPOMI satellite sensor. 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB 2019
10/12/2019
Installation of a new MAXDOAS instrument in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo Space-based measurements indicate that Central Africa is a global hotspot of formaldehyde (H2CO). This is due to biomass burning and to the emissions of the vegetation itself. African megacities also suffer from poor air quality associated with the widespread use of domestic combustion for cooking and old car fleets, which lead to large amounts of PMs and NOx. Due to the rapid demographic growth, the air pollution is expected to further deteriorate in African megacities. There are thus clear interests for local measurements in megacities of Central Africa, from scientific but also public health perspectives. 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB
23/08/2019
S5PVAL-BE campaign For validation of the recently launched Sentinel-5 Precursor (S-5P) / TROPOMI mission, the S5PVAL-BE campaign took place from 26 to 29 June, 2019 over Antwerp and Brussels, Belgium, with a focus on mapping of the horizontal distribution of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2). In total four mapping flights, coinciding with the S-5P overpass time, took place on four consecutive, cloud-free days with the APEX imaging spectrometer. The analysis of the gathered data will focus on the assessment of the TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 product over polluted regions as well as on the TROPOMI sub-pixel NO2 variability and the impact of spatial smoothing of the signal. 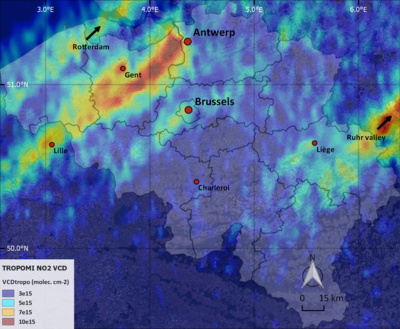
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB
05/04/2019
FRM4DOAS: A centralized MAX-DOAS processing system in support of satellite validation To harmonise the MAXDOAS data sets measured all over the world, the Fiducial Reference Measurements for ground-based DOAS Air-Quality Observations (FRM4DOAS) project was set up as a demonstration project providing a centralized rapid-delivery (24 hour latency) processing service for a selection of MAX-DOAS instruments.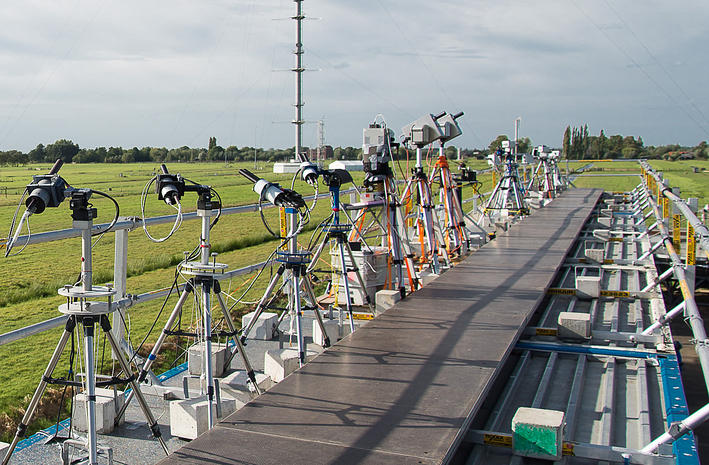 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB 2018
11/07/2018
Sentinel-5p: first TROPOMI air quality measurements On 19 June 2018, a press conference was held at BIRA-IASB to present the first results from the TROPOMI instrument on-board the Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite. TROPOMI, (the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument has been monitoring the whole of Earth's atmosphere on a daily basis ever since its launch in October last year. Belgian scientists are strongly involved in the analysis of the data and can now present the first formidable results of the instrument's air quality measurements. 
Ⓒ BIRA-IASB/DLR/ESA/EU 2017
01/12/2017
Sentinel-5p first light: first TROPOMI results. Today, the first scientific results were presented from measurements of the TROPOMI satellite instrument, launched last October on-board the Sentinel-5P platform. During an ESA press event, organised at the German Aerospace Center DLR, a range of images and animations were shown, demonstrating the unprecedented spatial resolution delivered by the TROPOMI sensor. 
source: ESA
17/10/2017
Sentinel-5p/TROPOMI: Mapping air quality in unprecedented detail Last week, on October 13, 2017, the European satellite Sentinel-5 Precursor (Sentinel-5p) was launched from the Russian Cosmodrome of Plesetsk on behalf of the European Space Agency (ESA). Its payload contains a single instrument, the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI), that is designed to analyse the chemical composition of the Earth's atmosphere in unprecedented detail. The UV-VIS/DOAS group and other scientists from the Royal Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (BIRA-IASB) are strongly involved in the analysis of TROPOMI's data. source: ESA
10/08/2017
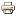
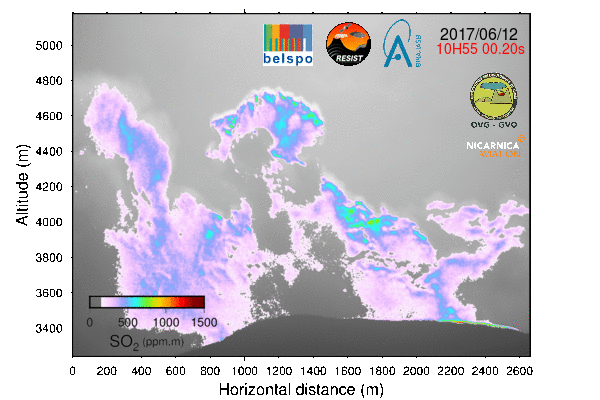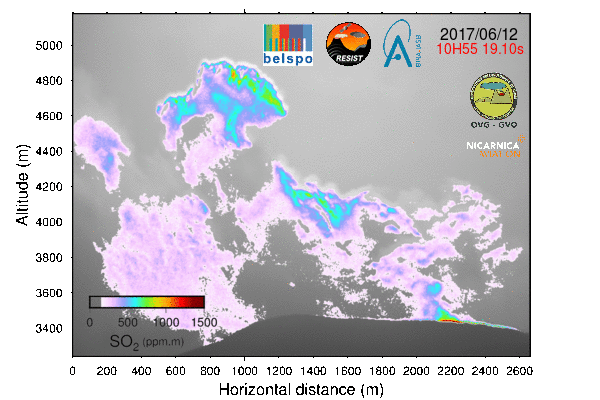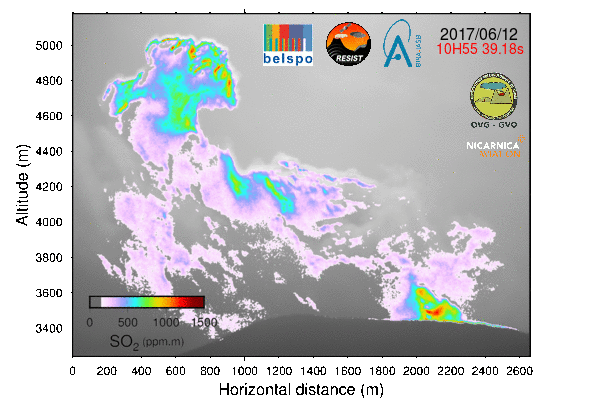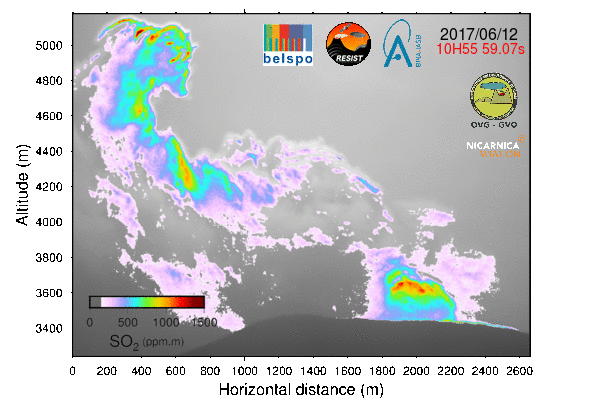
Expedition in Congo In June 2017, the BIRA-IASB UV-Vis DOAS group participated in a 12 day scientific measurement campaign in and around the main crater of the Nyiragongo volcano (in the Virunga Volcanic Province, Democratic Republic of Congo) as part of a BBC documentary expedition. The aim of the campaign was to collect scientific data with different types of instruments (seismic, infrasound detectors, temperature data loggers, weather stations, and several types of cameras) in order to better understand the physical mechanisms that drive volcanic processes in the region. This multidisciplinary campaign included 15 scientists from ECGS, EPIC, BSU, GVO, KMMA-MRAC, ULg/UH and BIRA-IASB. 2016
01/09/2016
The CINDI-2 Campaign In September 2016 our team will participate in the CINDI-2 campaign, to be held in Cabauw, the Netherlands. CINDI stands for Cabauw Intercomparison of Nitrogen Dioxide Measuring Instruments and involves the comparison of a host of ground-based DOAS instruments for measuring atmospheric Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) amounts...
19/05/2016
The AROMAPEX campaign The AROMAPEX campaign was held in Berlin in April 2016. AROMAPEX was supported by the European Commission through Eufar and by the European Space Agency (ESA) in the framework of its Copernicus Earth observation programme. The campaign was coordinated by BIRA and included 12 research groups from Belgium (BIRA, VITO), Germany (Universities of Berlin, Bremen, and Heidelberg, MPIC, DLR), Romania (INCAS, University of Galati), and the Netherlands (University of Delft, KNMI, TNO). 2015
30/11/2015
Installation of a MAXDOAS instrument in Antarctica Belgium has a long history of Antarctic exploration and scientific activities, dating back to the first expeditions to Antarctica under the lead of Adrien de Gerlache in 1897. BIRA-IASB already operates a CIMEL instrument since February 2009 at the Princess Elisabeth station. In the frame of the AEROCLOUD project, Christian Hermans will install a MAXDOAS instrument this winter (December 2015). The BIRA MAX-DOAS and the sunphotometer are highly complementary, since their synergistic use provides information on integrated and vertically resolved aerosol properties.
23/09/2015
The AROMAT-2 campaign.
The second Airborne ROmanian Measurements of Aerosols and Trace gases (AROMAT-2) campaign was
held in Romania during the second half of August 2015...
Read more
22/07/2015
Belgian urban NO2 monitoring based on APEX remote sensing
On April 14 and 15, 2015 a curious plane could be spotted above Belgium.
The Dornier DO-228 airplane, operated by Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR),
was carrying out measurements with the Airborne Prism EXperiment instrument.
APEX is an airborne pushbroom hyperspectral imager developed by a Swiss-Belgian consortium on behalf of ESA.
The objective of this campaign is to map the nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
spatial distribution at high resolution... Read more
24/04/2015
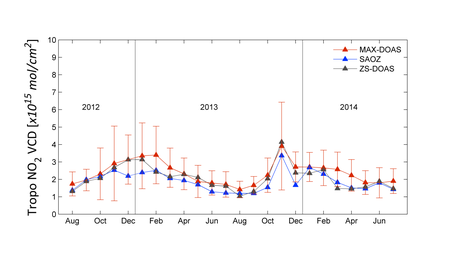
NO2 VCDs from zenith-sky DOAS.
Recently a new algorithm for retrieving tropospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
vertical column densities (VCDs) from ground-based zenith-sky (ZS)
measurements of scattered sunlight was published in AMTD. The method is
based on a four-step approach consisting of... Read more
23/02/2015
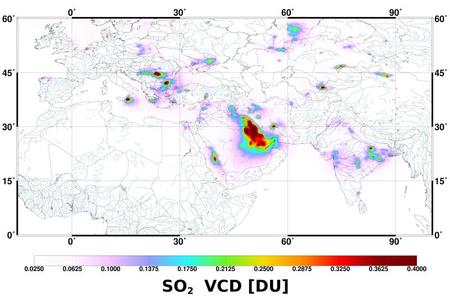
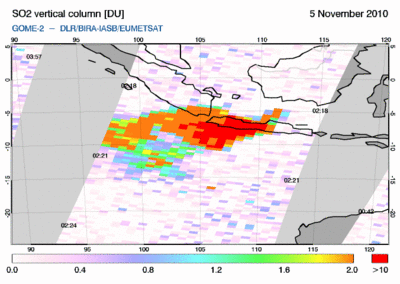
New OMI SO2 vertical column data set
In preparation of the upcoming TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor mission, we
have developed a new retrieval algorithm for SO2 vertical columns and
applied this scheme to 10 years of observations by the OMI/Aura
instrument... Read more 2014
05/12/2014
The AROMAT Campaign
The Airborne ROmanian Measurements of Aerosols and Trace gases (AROMAT)
campaign was held in Romania during the first two weeks of September
2014. AROMAT took place in the framework of the ESA Copernicus Earth
observation programme and was coordinated by BIRA. AROMAT included seven
other research institutions from Romania (University of Galati, INOE, and
INCAS), Germany (Universities of Bremen, Berlin, and MPIC) and the
Netherlands (KNMI).
read more
27/10/2014
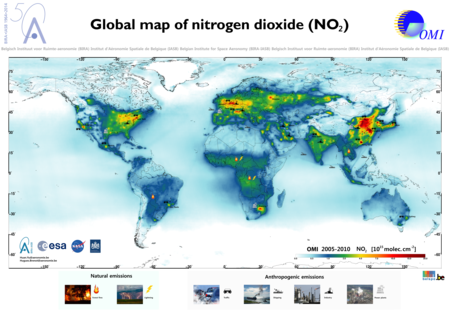
High resolution global maps of trace gases from OMI
In the framework of the preparation of the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor (S5-P)
mission, which is planned for launch in early 2016, UV-Vis retrieval
expert scientists at BIRA-ASB have been working on the derivation of high
quality tropospheric trace gas data products derived from the heritage
Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) flying on board of the NASA AURA
platform since 2004.
read more
18/02/2014
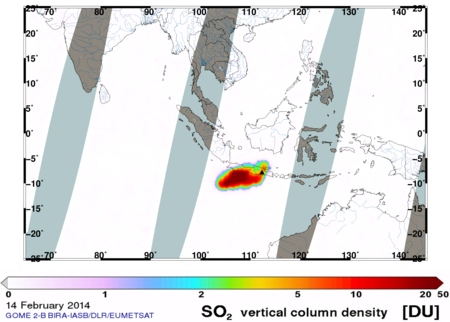
The eruption of Kelut
The Kelut eruption on the island of Java has produced a large ash and SO2
cloud that has been tracked by polar orbiting satellite instruments (IASI
and GOME-2 onboard MetOp-A and MetOp-B, OMI on Aura, and AIRS on
Aqua). The ash has reached high altitudes where commercial aircraft fly
and is a significant hazard to aviation. Three airports on Java have been
closed and air routes from Australia to Singapore, Bangkok and beyond affected.
read more
16/01/2014
Installation of a MAXDOAS and a CIMEL in Burundi
End of November 2013, BIRA-IASB has installed a MAXDOAS instrument and a CIMEL photometer at the top of the Sciences Department of the University of Burundi at Bujumbura. 
2013
06/08/2013
The MAD-CAT Campaign
From 7 June until 5 July 2013, BIRA-IASB participated in the "Multi Axis
Doas - Comparison campaign for Aerosols and Trace gases" (MAD-CAT) in Mainz, Germany.
... read more 
18/03/2013
PhD thesis defence of
Alexis Merlaud: Development and use of
compact instruments for tropospheric investigations based on optical
spectroscopy from mobile platforms
read more 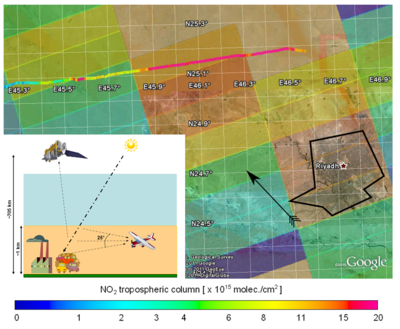
2011
28/11/2011
Trend of stratospheric NO2
read more 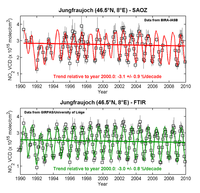
23/05/2011
The May 2011 Grímsvötn eruption
read more 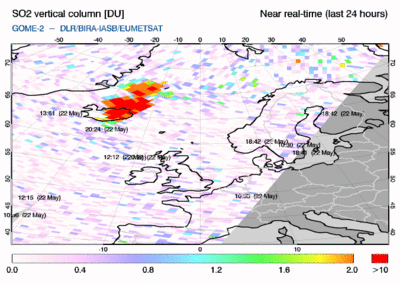
2010 2009 2008
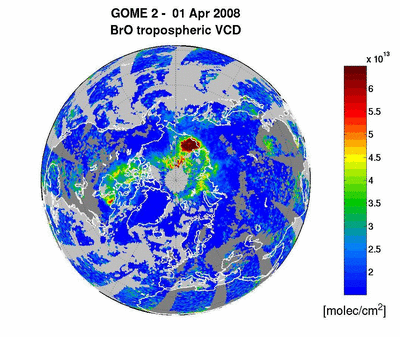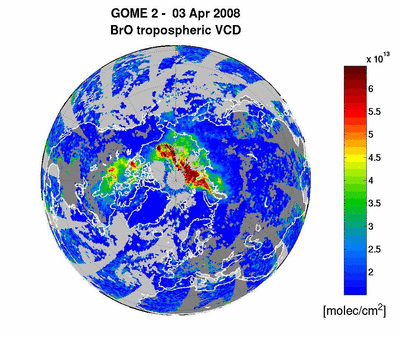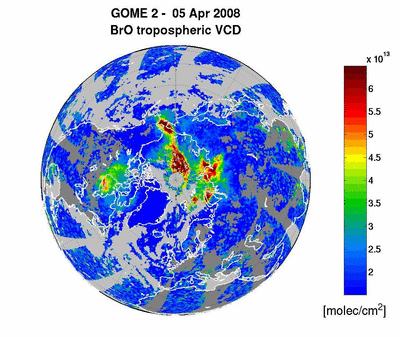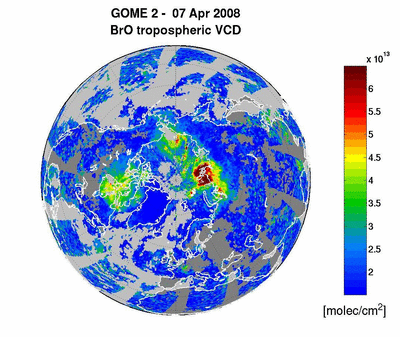
20/10/2008
METOP-1/GOME-2: BrO emission from
the Kasatochi Volcano (Alaska) 06-16 August 2008 read more 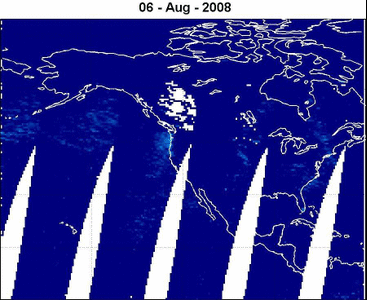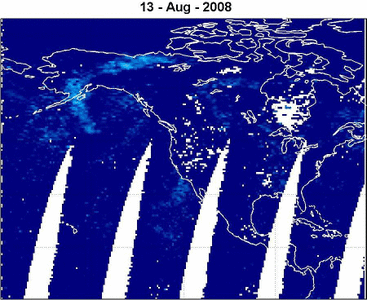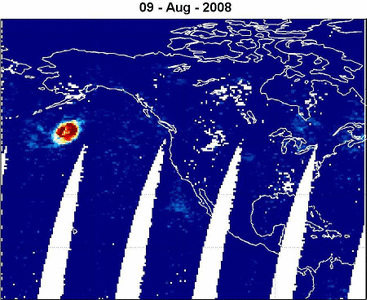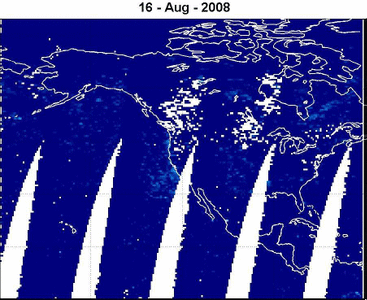
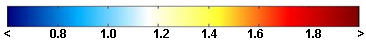
BrO VCD [ x1014 molecules cm-2 ]
© Nicolas Theys
|