|
~ Ground-based:
|
Ground-based Observations The experience of BIRA-IASB in atmospheric research activities using ground-based UV-Visible DOAS spectrometers goes back to the early nineties. The aim of the research is the long-term monitoring of the minor components involved in the catalytic destruction of the ozone layer and the study of anthropogenic pollution. BIRA-IASB operates several UV-Visible instruments, both during specific campaigns and continuously at different stations 
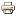
Location of the BIRA-IASB UV-Vis instruments BIRA-IASB stations BIRA-IASB measures at the eight stations enumerated above in the framework of the NDACC (Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Composition Change). BIRA-IASB campaigns BIRA-IASB also participated to the following international field campaigns:
BIRA-IASB instruments These UV-Vis instruments are based on Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS, Platt 1994). The evolution of the traditional passive zenith sky technique (allowing the monitoring of stratospheric components, such as the O3 and NO2 and minor trace species like BrO and OClO)and the development of Multi-Axis instruments (MAXDOAS), allows the measurement of tropospheric pollutants and ozone precursors, like NO2, HCHO, O4, IO, CHOCHO and SO2. This newly developed remote sensing technique has a largest sensitivity towards the boundary layer and is ideally suited for the study of a layer close to the ground and thus for studies related to air quality issues. BIRA-IASB recently developed a "new generation" of MAXDOAS instruments, described here. NDACC recommendations for total O3 column retrieval in the visible Chappuis bands Read me :
Cross sections :
O3 AMF look-up tables :
O3 column averaging kernel look-up tables :
NDACC recommendations for stratospheric NO2 UV-vis measurements Read me :
NO2 AMF look-up tables :
NO2 column averaging kernel look-up tables :
|