 |
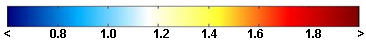
| BrO VCD [ x1014 molecules cm-2 ] |
The eruption of the Kasatochi volcano in Alaska on 7th August 2008 released
a large amount of BrO (and other gases, such as SO2) in the atmosphere which could be followed by the
GOME-2 instrument during several days after the eruption.
Lagrangian dispersion modeling results, based on the FLEXPART tool, show that the volcanic
BrO was directly injected in the upper troposphere/lower stratosphere at altitudes ranging
from 8 to 12 km, and that the total mass of reactive bromine released in the atmosphere was
around 50-120 tons.
These results represent the first space-based observation
of BrO emissions due to volcanic activity.
Reference:
Theys, N., M. Van Roozendael, B. Dils, F. Hendrick, N. Hao, and M. De Mazière (2009),
First satellite detection of volcanic bromine monoxide emission after the Kasatochi eruption,
Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L03809, doi:10.1029/2008GL036552.
Relevant links:
ESA news item on Kasatochi BrO
FLEXPART
Kasatochi Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission
Kasatochi at the
Alaska Volcano Observatory
Contact:
Nicolas Theys
|