|
~
|
Participation to the POLARCAT activity The POLARCAT-France spring campaign took place between 30 March and 11 April 2008 as part of the POLARCAT international research activity (Polar Study using Aircraft, Remote Sensing, Surface Measurements and Models, of Climate, Chemistry, Aerosols, and Transport), in the framework of the International Polar Year (IPY).
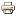
Flights on 8 April 2008 and 9 April 2008 of the POLARCAT-FRANCE Spring campaign Based in Kiruna, Sweden, the Safire ATR-42 aircraft performed twelve scientific flights between continental Norway and Svalbard. Scientific objectives of the campaign included the study of pollution transport, aerosol/cloud interactions and satellite validation.

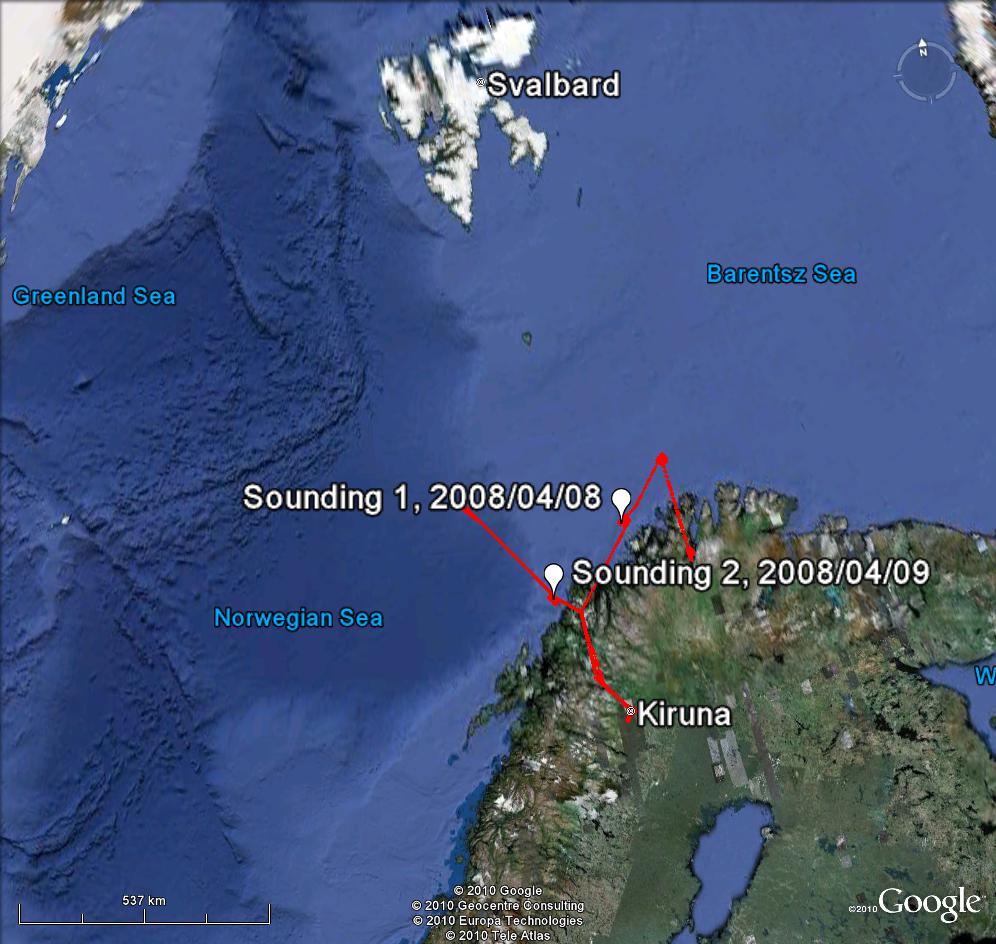
Picture taken from the ATR-42 on 8 April 2008, above the North Cape Area The Airborne Limb Scanning DOAS (ALS-DOAS) was developed at the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (BIRA-IASB) and first used during the POLARCAT campaign. It records limb-scattered sky light spectra at several angles around the horizon, following the Multi-axis DOAS principle.
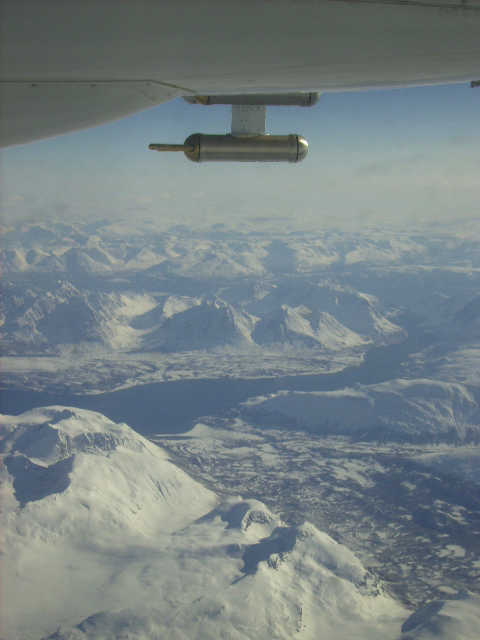
The ALS-DOAS instrument onboard the Safire ATR-42 Several tropospheric molecules absorb light in the spectral range of our instrument and thus are potentially detectable: O3, NO2, HCHO, CHOCHO, O4, IO and BrO. In the POLARCAT data, we have focused on O4 and NO2 measurements, which were most clearly identified during the campaign. The O4 measurements were used to retrieve the aerosol extinction and used as an input for the aerosol loading in the retrieval of NO2. Both retrievals are based on a maximum a posteriori approach. We have compared a gaussian a priori with a lognormal one, which constrains the solution to positive values. The latter yields, in our cases, extinctions which are closer to independently measured size distributions.
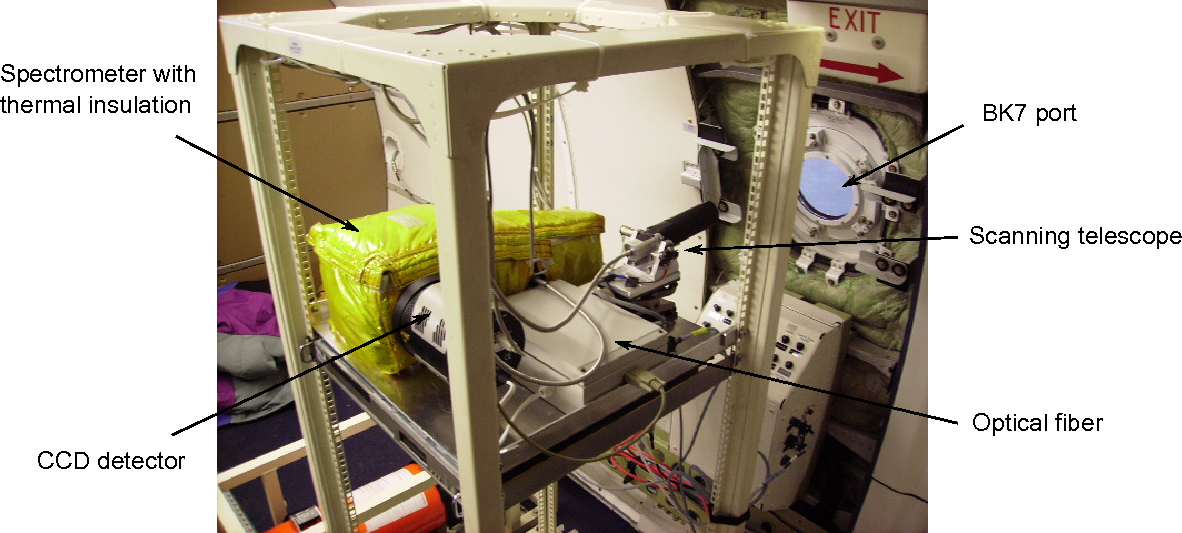
Example of results: retrieved NO2 profile for the sounding of the as0833 flight (9 April 2008). The measured vertical distributions are interpreted from CO and ozone in-situ measurements complemented by back-trajectories.
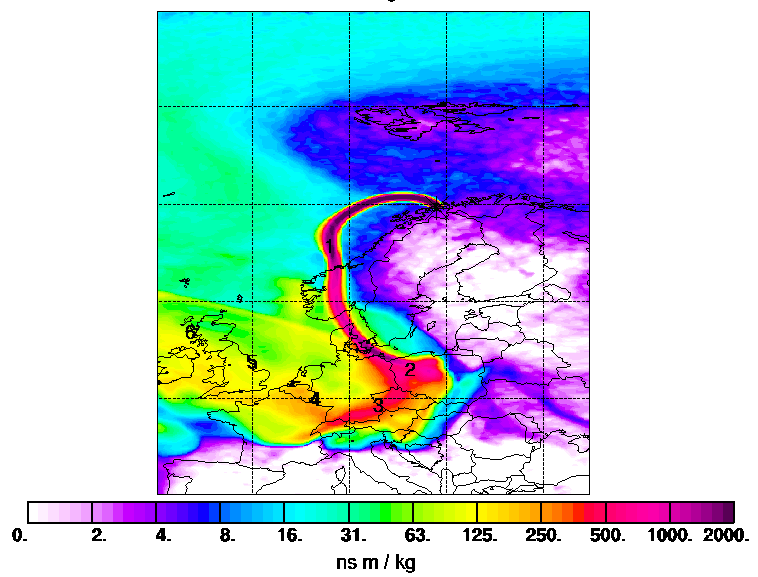
Column-integrated emission sensitivity as calculated with FLEXPART, for the 9 April 2008.
The NO2 layer at 4 km altitude observed on 9 April 2009 seems to have been directly transported
from central Europe with CO and aerosols.
Publications Merlaud, A., Van Roozendael, M., Theys, N., Fayt, C., Hermans, C., Quennehen, B., Schwarzenboeck, A., Ancellet, G., Pommier, M., Pelon, J., Burkhart, J., Stohl, A., and De Mazière, M.: Airborne DOAS measurements in Arctic: vertical distributions of aerosol extinction coefficient and NO2 concentration, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, 9219-9236, doi:10.5194/acp-11-9219-2011Acknowledgements and links This work was supported by the Belgian Federal Science Policy (contract MO/35/028). The installation of the ALS-DOAS in the Safire ATR-42 and our participation to POLARCAT were funded by EUFAR through the POLUVIS project.
Contact For more information, please contact : Alexis Merlaud or Michel Van Roozendael |